Forearm Instability: Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Treatment Options
Fuente
Este artículo es originalmente publicado en:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28052828
http://www.jhandsurg.org/article/S0363-5023(16)30895-4/abstract
De:
J Hand Surg Am. 2017 Jan;42(1):47-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2016.10.017.
Todos los derechos reservados para:
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Surgery of the Hand. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Abstract
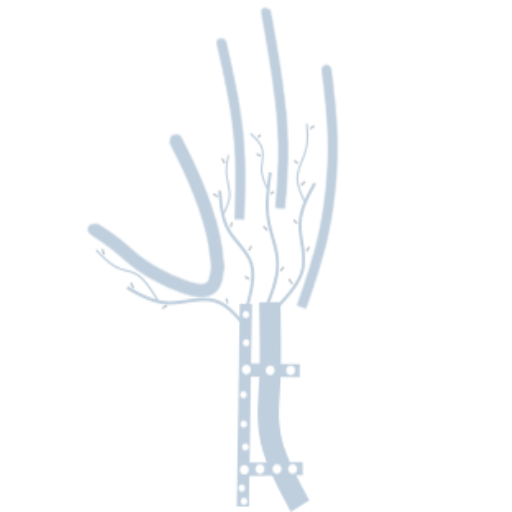
The forearm unit consists of the radius and ulna, a complex and interrelated set of joints (distal radioulnar joint, proximal radioulnar joint) and the soft tissue stabilizers between the 3 bones. Distally, this is represented by the triangular fibrocartilage complex at the wrist, proximally by the annular ligament at the elbow, and in the forearm by the interosseous membrane. Disruptions in any of these structures may lead to forearm instability, with consequences at each of the remaining structures.
Resumen
La unidad del antebrazo consiste en el radio y el cúbito, un conjunto complejo e interrelacionado de articulaciones (articulación radioulnar distal, articulación radioulnar proximal) y los estabilizadores de tejido blando entre los 3 huesos. Distalmente, esto está representado por el complejo triangular fibrocartílago en la muñeca, proximalmente por el ligamento anular en el codo y en el antebrazo por la membrana interósea. Las interrupciones en cualquiera de estas estructuras pueden conducir a inestabilidad del antebrazo, con consecuencias en cada una de las estructuras restantes.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Surgery of the Hand. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
KEYWORDS:
Essex Lopresti; Forearm instability; Galeazzi fracture; Monteggia fracture